DCL Electric Actuator - Wuhan Huayi Technology Co. > Technical Support > How do actuators with bus functions work? -Modbus, CAN, Ethernet, Profibus
How do actuators with bus functions (motorized valves) work?
-Modbus, CAN, Ethernet, Profibus
When you install DCL with bus function for electronically controlled valves on the pipeline, you can control a group of electronically controlled valves via bus (Modbus, CAN, Ethernet, Profibus), thus realizing synchronous control of valve clusters.

Using the bus Control of DCL actuators
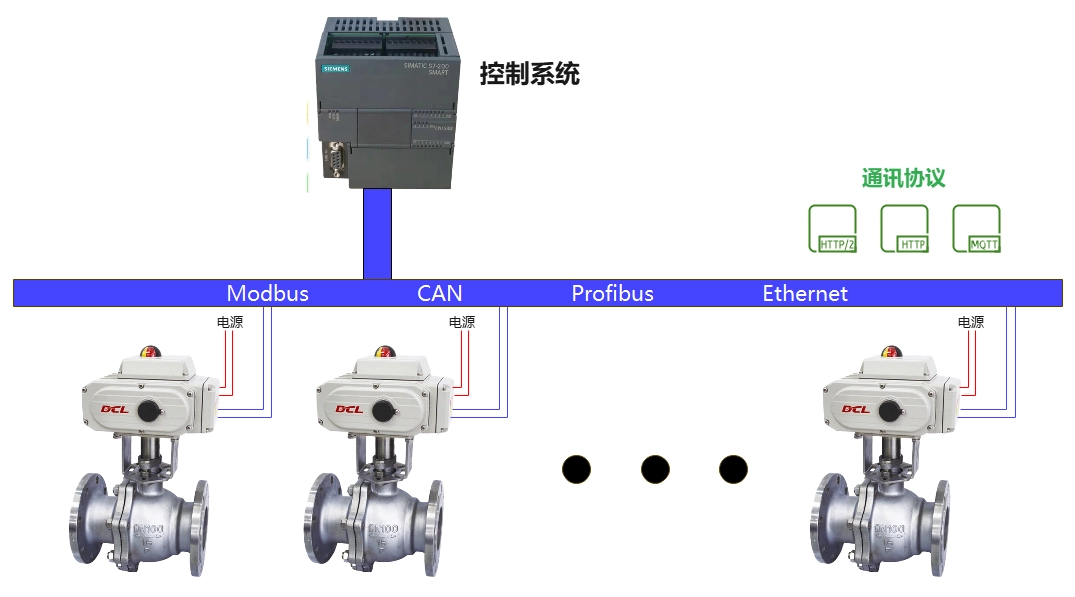
- The control system sends opening control commands to the actuator through the bus communication protocol. The actuator follows the bus command to drive the valve to the specified opening.
- If a bus error occurs, the valve is actuated to fully open, fully close, or maintain the valve position at the time of the bus error, depending on the user setting.
- If the power supply to the power line stops while the actuator is driving the valve, the actuator stops driving and the motorized valve maintains its current position.
NOTE: The above circuit diagram shows the function of a switching actuator (motorized valve) in its simplest form. In practical applications, additional protection devices such as fuses and current limiters should also be considered.
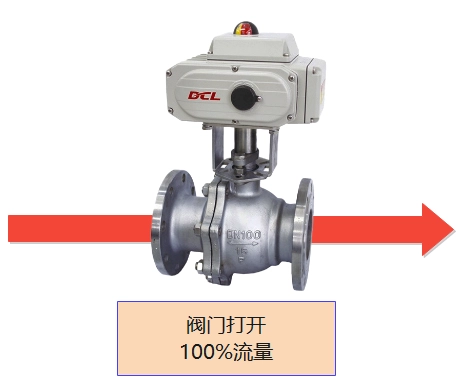
3 states


Learn more
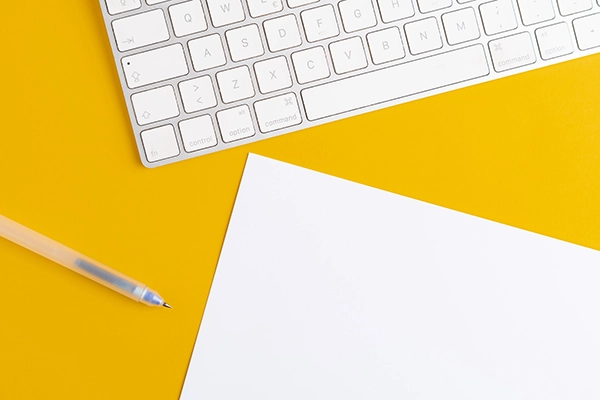
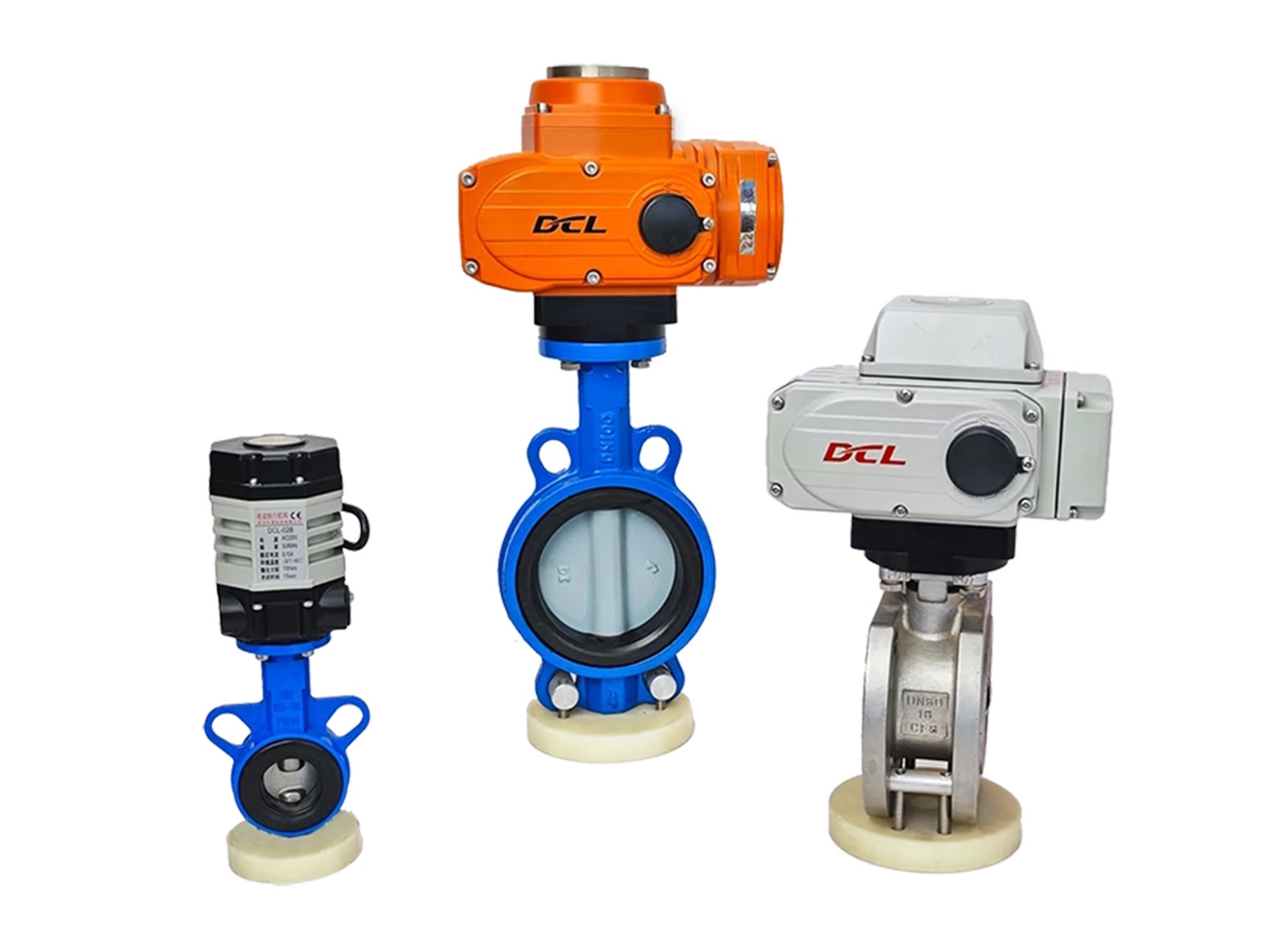
Selection of DCL electric actuator
Torque: 20-600Nm
Time: 4S~60S
Angle: 0~90° | 0~360°
Torque: 20-2500Nm
Time: 4S~75S
Angle: 0~90° | 0~360°
Torque: 12-1200Nm
Time: 2S~12S
Angle: 0~90° | 0~360°
Torque: 9-18Nm
Time: 7S~60S
Angle: 0~270°




























 Egong.com.cn 42018502006527 No.
Egong.com.cn 42018502006527 No.